Mi'kmaw Kina'matnawey
2 months (2018)
Interact with the high-fidelity prototype (1 user flow) here
The B2C mobile apps for learning the indigenous Mi’kmaw language was finding a hard time in retaining its users and the marketing metrics were on sloping downwards.
The users were not comfortable learning a new language from a mobile application with a book-like user interface.
The need of the hour demanded a single application, one that is heavily supported by cognitive and market research with a targeted experience strategy.
UX Researcher & Information Architect
• Led a team of 4
• Language learning immersion research & strategy
• Human information processor's cognitive load reduction
• Tactical research but in a waterfall project method
• One man UX
• First attempt in UI design (Hi-Fi prototyping)
increase in
recall rate.
task completion rate
average filling time.
distinct
user personas.
Existing product research:
• User feedback analysis
• Moderated usability testing (Formative & Summative)
• Language learning principles & usability heuristics evaluation
Exploratory research:
• Human cognition's function in Second language learning - literature review
• User personas
• Task flows
• Brainstorming based sketching (NEW)
Synthesis:
• Information architecture
• Paper sketches
• Rapid Prototyping - Lo-Fi & Hi-Fi prototyping
New (re-designed) product research:
• Language learning principles & usability heuristics evaluation
• Guerrilla tests (moderated in-person usability testing)
• Remote moderated navigation tests
• Figma
• Adobe XD (for wireframes)
• Adobe Illustrator
• Adobe Photoshop
• Design system - Based on 'Human Interface Guidelines'
• Make users trust again (Nothing to do with politics here 😅)
• Need for highly efficient tactical research methods
• Short time period (2 months)
• UX designer (myself)
• Native app developer - Android and iPhone
• Business analyst
• Mi'kmaw language expert
To tackle the lack of acceptance from the end-users, a room to reform the user experience massively through immersive learning awaited.
User experience plays a vital role in bringing immersion in second language learning, especially in mobile applications.
In this project, UX flourished especially at the intersection of research, technology, cognition & strategy.
Since the project was short spanned and a demand for evidence-based research mounted high, classic waterfall methodology was adopted. The quick iterations used in design operations was similar to agile but didn't involve a complete framework.
Why?
- To find research insights from literature in order to test basic cognitive principles through MALL, CALL & SLA.
- Find the pitfalls in the existing product(s).
- Self-initiated tactical research helped in prioritizing problems-to-be-solved.
Results:
• Tactical research insights increased values to devise strategies in short time.
The user research that was performed was classified into two categories, namely, existing research findings (~65% research) and basic user research practices (~35% research).
For this short duration, the data from similar existing research played a vital role. The 3 guiding principles in language learning cognition’s research pool was a powerful place to begin with.
• SLA - Second Language Acquisition.
• MALL – Mobile assisted language learning.
• CALL – Computer assisted language learning.
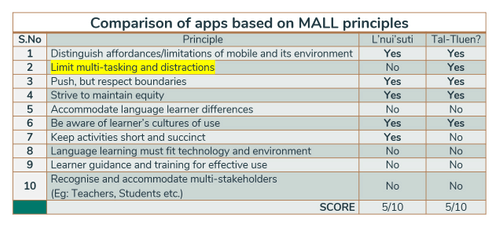
The Begay (2018) & Stockwell (2013) rubrics helped in evaluating the existing apps to target major pain-points in human cognition.
Significant qualitative data was extracted from user reviews from the Playstore and Appstore. Manual analysis of the data was done (since the quantity of the data was less) and I drafted the pros and cons to be focused for improvement.
• Make Mi’kmaw language learning possible for a large user base and increase user retention for strengthening the language in the community (multi-purpose).
• Enable virtual immersive learning possible through enhanced mobile second language learning.
Why?
- Understand and educate the team in how human cognition works in learning a second language.
- Discover the possible points where a mobile application can provide an added advantage in second language learning?'
Results:
• Introduced the concept of immersion to the design, development and business stakeholders.
• Square on simple features with large impact.
User research gave rise to 3 major factors that can be implemented in the mobile app. The following points were key factors that was considered to create immersion.
This forms the major part of a second language learning in a mobile environment. A user who tries to learn a new word or looks for a previously learned word uses a known primary language (in this app - English) to learn the new word.
The fundamental concepts to immerse a user in second language learning involves audio and visual encoding. The immersion can be text, audio and images placed separately within the same screen or use a video with subtitles to cover all aspects.
Revising is an important concept to prolong the memory of a learned word or a sentence. Revision can be classified into immediate revision (right after learning), periodical revision (re-learn the learnt at regular intervals) and sporadic revision (re-learn/remind the learnt at irregular intervals ). Each has it's own benefits based on the need and application scheme.
Why?
User personas & Task Flows:
Find out 'most valuable experience' dedicated for this app.
Brainstorm using sketches:
- Identify and classify users' mental models.
Results:
• Aggregated the users' mental models to form the base of IA design.
The research paved way to determine 3 inter-linked ideation methods.
1. Creating personas & exploring the possible task flows from the results from research.
2. Brainstorming user-generated sketches to visualize the user's expectations & understand users' mental models.
3. Finally, construct the info architecture based on the gathered insights.


Why?
To introduce 'Progressive disclosure' in the IA based on the aggregated mental models.
Results:
• An IA with high situational awareness.
• Most common test cases (possible) drafted to QA team

Why?
- Introducing focus in a device that is used for instant gratification.
- Multiple modes of encoding to secure 'Sensory information transfer' channels.
Results:
• Secure user's sensory and perception lines.
• Proper use of encoding factors.
• Most common (possible) test cases gifted to the QA team.
Why?
- Activate and store learnt information in long term memory.
- Ground-zero features that keep users engaged in a gamified environment
Results:
• Enhanced retention (long term memory)
• Improved recall rates
(Check results section for numbers)
.png)
Why?
- Quickly validate designs
- A precursor for usability testing
Results:
• Rapid iterations to re-design after every changes
Why?
- Introducing the prototypes to the users for testing the initial acceptance.
- Testing random users for fixing unknown defects.
Results:
• Found, rectified and iterated minor defects before moving into production.
The acquisition rate which was tested by recall tests at the end of guerrilla testing drastically increased by ~200%. This gave a clear understanding of the impact of cognitive theories in UX & immersive learning.
The fluid navigation gave rise to high situational awareness rates. All 12 participants navigated successfully for 10 destinations challenged. The feedback specified that the signifiers at specific positions in the navigation design was the most compelling reason for this feat.